Fast fashion is out. Renting and resale will become the new normal.
Photo by Lauren Fleischmann on Unsplash
Around the globe people become more aware of the trade off between buying fashion items, wearing them a few times, disposing and what it does do our planet. Many new (online and physical) retail platforms have started concentrating on second hand items and renting out. Some even say that the second hand fashion market will outgrow fast fashion by 2028.
The end of ownership.
Second to oil, the clothing and textile industry is the largest polluter in the world. The carbon footprint from textiles production in 2015 was greater than the CO2 equivalent of international flights and shipping combined. Three-quarters of our clothing will end up burned or buried in landfill. Some say that more than half of the fast fashion produced around the world is thrown away within one year. New circular techniques are being used in the production processes. But in a world where people are more conscious and aware of what and why they buy, it is normal that new retail concepts enter the market place. Enter, second hand and rental.
Resale and rental are changing the script.
Fashion is big, really big. The world market is estimated around $1,3 trillion, bigger than Russia's GDP. The market of resale fashion is tiny, but developing quite fast. From just thrift stores and buying on platforms as e-Bay, to a vast array of new brands. Resale apparel used to be the domain of bargain hunters, some were treasure hunting. Now early adaptors are browsing the many new (online) platforms entering the market place.
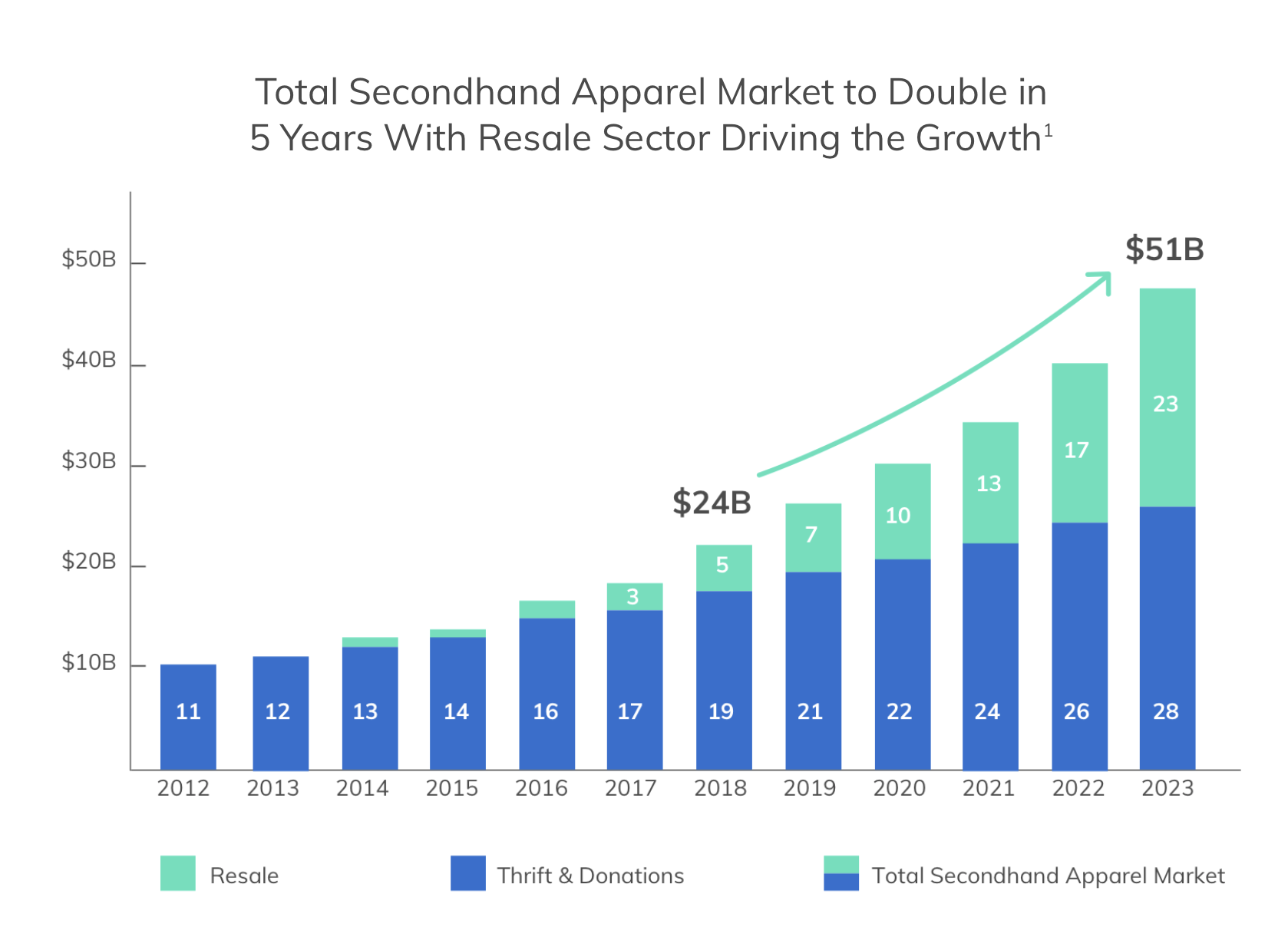
Some crucial facts and data from US based Thredup:
the US resale market will grow from $7bn in 2019 to $23bn in 2023
including already existing thrift stores total market will grow to $51bn by 2023
resale apparel has grown 21x faster than the retail apparel market in the last 3 years
2/3 of all women shoppers have bought or are willing to buy resale
40% of consumers now consider the resale value of an item before buying it, a 2x increase from 5 years ago
Millennials and Generation Z are adapting 2.5 times faster, compared to other groups.
second hand, rental and subscription are projected to be the top 3 fastest growing categories in the 2019-2028 timeframe
in 2018 the US fast fashion market was $35bn, compared to $24bn for second hand. By 2028 the second hand market will have grown to $64bn, whereas fast fashion's growth is projected at $44bn
According to Mintel 44% of young women said they would like tone more eco friendly in their approach to fashion
Why own stuff?
There are multiple drivers for this massive shift. There is the obvious penetration of social media and the importance of influencers. Female fashion buyers are increasingly savvy on updating their wardrobes to the latests crave of the catwalks. With real buying power mostly being flat, in many economies, this obviously create tension. Add the increasing consciousness on sustainability and the fact that a new perception has been growing on possession and ownership (why own stuff?, aka the sharing economy), it's easy to see why things are moving. Some also mention smaller housing as a driver for change, with the average number of items in consumers' closets declining from 164 items in 2017 to 136 in 2019.
Elizabeth Cline, author of the Conscious Closet: “Resale offers the wardrobe-rotating fun of fast fashion without the guilt or waste. By driving preferences away from disposable fashion towards higher-quality clothes, reuse is a boon for our personal style and the planet.”
Rental is different, a closet in the cloud.
For many online fashion retailers "wardrobing" or "ASOS parties" are a huge problem. The demand for fresh looks is prompting many people to order online, wear it and return it later ("after the party"), often for free. Fashion industry returns hoover around 40-50% of items being bought online. Many new platforms persuade consumers from wardrobing into hiring. The US apparel rental market is relatively small, estimated to grow to $4,4bn by 2028, just 1% of total clothing sales. But it grew 24% in 2018 compared to 5% for the wider clothing market, GlobalData shows.
These rental platforms are buying clothing wholesale from brands, some are introducing revenue sharing models allowing brands to upload items, the platform taking care of cleaning and delivery in return for a share of revenue.
Rent the Runway redefined the fashion rental market already in 2009, starting with one offs like a dress for a gala. Many platforms have evolved now to a monthly subscription model and are positioned mostly upmarket. Some even IPO-ed recently, because investors love the recurrent revenues of the subscription business model.
Some examples. Both second hand and rental. Physical and online.
Round Two
The diversity of brands and formats serving second hand and rental customers is immense. Round Two in the US is a resale outlet, with only two stores. A tactile experience with overflowing racks, but not as in the old thrift stores, where you would occasionally meet a bargain hunter. Round Two is different, young people and kids are roaming the racks, with brand new items and slightly worn ones. A brand new $300 T-shirt by Supreme, next to a vintage bootleg Janet Jackson T-shirt ($250) . It's a place where you can buy and sell. Nothing is on consignment (in that case the seller retains ownership).
Vintage Brands store in Monnickendam (Netherlands) is doing the same as Round Two, though aimed at a different customer. Yearly over 700 women offer their personal fashion and accessory items, from Zara to Gucci, in consignment in this cosy store. Loyal customer find an extra reason for visiting the store: the social aspect is important, talking with the owner and other customers, on what's "new" and hot. You can sit down and read a magazine, drinking coffee. Sellers are often buyers. Vintage Brands' main marketing channel is word-of-mouth and social with a look book on Facebook and Instagram. The annual catwalks are famous and people drive over 100 miles to see models showing off.
Hirestreet is the UK first high street rental service and aims at budget conscious students. Hirestreet offers 10 day rentals for prices as low as £7. Most stock refreshes every week. Users will enter event date and choose outfit filters (with the "occasions" filter ranging from date night to maternity...) and Hirestreet will generate available rentals. Isabella West from Hirestreet found out that young women were spending over £500 a year on fast or disposable fashion and if they hired rather than bought they could save £400: "I found this amazing. £400 is the price of a holiday."
In the US the two dominant platforms are Rent the Runway and the RealReal, both very successful and growing fast. Rent the Runway (valued at $1bn) is a fashion subscription platform offering premium and exclusive fashion and accessories brands. It claims 10 million members. Its "unlimited plan" at $159 per month will offer unlimited access to as many items as a customer wants. If you love the idea of wearing premium brands like Gucci, Kates Spade and Diane Von Furstenberg RtR is a great option. RtR merchandise arrives in a garment bag with a prepaid UPS label for returns. Next to its platform they operate 5 stores and multiple drop off locations, but it is essentially a technology (and logistics) company. With the data being used both on the returns and via its "virtual closet" RtR is perfectly positioned to personalise its offering.
The RealReal is a premium luxury resale platform, with a Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) of $710mm in 2018, processing 1,6 Million orders from 400,000 different buyers. Items are authenticated and researched before being offered on its online platform or physical stores. In many cases professionals (authenticators) are visiting the seller, and discuss which items could be sold on the RealReal's platform, they are also advising on price. The merchandise is held in consignment for sellers. The company takes a 40 per cent cut of each sale, which is reduced for high-value items or for consignors who sell more than $10,000 per year. 56% of the RR's consignors count environmental impact as a key reason to sell on the platform. Buying a second hand Fendi bag for the price of the new Michael Kors bag ($300) is probably equally important.
In a complete reversal of things 7 years old Le Tote, a US based rental fashion platform, bought 190 years old Lord & Taylor department stores, some 35 locations located in the Midwest of the US. An old legacy company absorbed by a new one. Le Tote's proposition is different from RtR's. Most of its customers spend just $69 per month for mid-market brands like J Crew and Zara.
Meanwhile high street brands as Scotch & Soda, Rebecca Taylor and Urban Outfitters (with Nuuly) have started renting out items in a comparable scheme as RtR.
H&M could rethink it's $4bn unsold stock and put in on a rental platform. They just announced a limited rental service for its new premium collection from recycled fibers in a Stockholm store. Express, a fashion mall brand with 600 stores in the US, started a rental service with a $70 monthly subscription. Ikea even launched a furniture rental service earlier this year.
Rental and buying secondhand fashion is beyond icky.
So things are definitely moving. This business is beyond the icky feeling people used to have with wearing items somebody else had worn before. It's still early and it is probably harder to persuade consumers to hire affordable apparel than catwalk creations, just because there are just too many cheap alternatives available. Some platforms are growing too fast, causing some hiccups. With young and conscious consumers growing up and becoming more influential this will change. The sharing economy is here to stay.
Sources and graphs used from thredup.com, Reuters, Bloomberg, Wired, Forbes, the Guardian, New York Times, Vogue